Journal of IiME
Volume 2 Issue 2
www.investinme.org
Family Illnesses Among People with ME/CFS: Blood Versus Non-Blood Relatives
(continued)
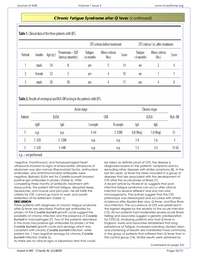
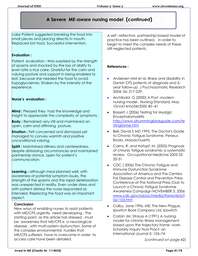
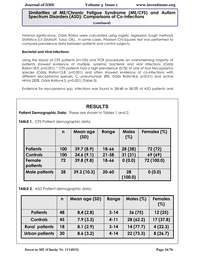
found 5 total cases of diabetes for all nonblood
relatives, whereas for the fathers of
people with ME/CFS, there were 20 cases.
These findings suggest that at least for
diabetes, the outcomes are not likely due to
there being more blood relatives than nonblood
relatives.
Furthermore, one could argue that a person
may have more non-blood relatives than
blood relatives. According to the United
States Census Bureau (2000), the average
family size in the United States is 3.14. Using this
statistic, after four generations of two parents
having one child, a fourth generation person
would have 14 blood relatives. These 14 blood
relatives are the person’s: 8 great
grandparents, 4 grandparents, mother and
father. However, when this individual marries
their spouse, assuming their spouse is also a
fourth generation person from one child
families, this individual will gain 15 non-blood
relatives. These 15 non-blood relatives include
their spouse, and their spouse’s 8 great
grandparents, 4 grandparents, and 2 parents.
Therefore, it is at least conceivable that there
might be as many non-blood relatives, if not
more, than blood relatives.
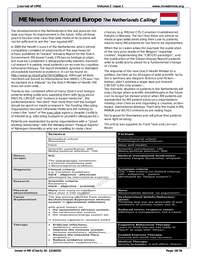
In general, the findings of this study found that
family members who are related by blood
have several medical illnesses at higher rates
than those who are non-blood related.
Certainly, the findings are strongest for
diabetes, and it is always possible that recall
bias influenced the results. However, the
robust nature of the outcomes indicates this is
an area worthy of future investigations, and
having medical work-ups of both blood and
non-blood relatives would strengthen
research. There are policy implications of this
work, for if individuals with ME/CFS do have
blood relatives with more medical illnesses, it is
possible that both genetic and environmental
factors need to be considered when
understanding the etiology of this illness and
when providing treatment for those with this
illness.
Invest in ME (Charity Nr. 1114035)
References
Addington, J.S. (2000), 'Chronic fatigue
syndrome: A dysfunction of the
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Journal
of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, 7, 2, 63-73.
American Diabetes Association. (2008).
Diabetes Statistics. Retrieved June 26, 2008,
from www.diabetes.org/diabetes-statistics.jsp
Bates, D.W., Buchwald, D., Lee, J., Kith, P.,
Doolittle, T., Rutherford, C., Churchill, W.H.,
Schur, P.H., Wener, M., Wybenga, D.,
Winkelman, J. & Komaroff, A.L. (1995), Clinical
laboratory test findings in patients with
chronic fatigue syndrome. Archives of Internal
Medicine, 155, 1, 97-103.
Brown, M.M. & Jason, L.A. (2007). Functioning
in individuals with chronic fatigue syndrome:
Increased impairment with co-occurring
multiple chemical sensitivity and fibromyalgia.
Dynamic Medicine, 6, 6 doi:10.1186/14765918-6-6.
Buchwald,
D., Cheney, P.R., Peterson, D.L.,
Henry, B., Wormsley, S.B., Geiger, A., Ablashi,
D.V., Salahuddin, S.Z., Saxinger, C., Biddle, R.,
Kikinis, R., Jolesz, F.A., Folks, T., Balachandran,
N., Peter, J.B., Gallo, R.C. & Komaroff, A.L.
(1992). A chronic illness characterized by
fatigue, neurologic and immunological
disorders, and active Human Herpesvirus
Type-6 infection. Annals of Internal Medicine,
116, 2, 103-113.
Cohen, J. (1988), Statistical Power Analysis for
the Behavioral Sciences, Hillsdale, NJ Erlbaum.
Demitrack, M.A., Dale, J.K., Straus, S.E., Laue,
L., Listwak, S.J., Kruesi, M.J.P., Chrousos, G.P. &
Gold, P.W. (1991). Evidence for impaired
activation of the hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal
axis in patients with Chronic Fatigue
Syndrome, Journal of Clinical Endocrinology
and Metabolism, 73, 6, 1224-1234.
Endicott, N. (1999). Chronic fatigue syndrome
in private practice psychiatry: Family history
of physical and mental health, Journal of
Psychosomatic Research, 47, 4, 343-54.
(continued on page 11)
Page 10/74
Journal of IiME
Volume 2 Issue 2
www.investinme.org
Family Illnesses Among People with ME/CFS: Blood Versus Non-Blood Relatives
(continued)
Freeman, R. & Komaroff, A.L. (1997). Does the
chronic fatigue syndrome involve the
autonomic nervous system? The American
Journal of Medicine, 102, 4, 357-64.
Friedberg, F. & Jason, L.A. (1998).
Understanding chronic fatigue syndrome: An
empirical guide to assessment and treatment,
Washington, DC, US, American Psychological
Association.
Fukuda, K., Strauss, S.E., Hickie, I., Sharpe,
M.C., Dobbins, J.G. & Komaroff, A. (1994). The
chronic fatigue syndrome: A comprehensive
approach to its definition and study, Annals of
Internal Medicine, 121, 953-959.
Green, S.B. & Salkind, N.J. (2003), Using SPSS
for Windows and macintosh: Analyzing and
understanding data (3rd Edition), New Jersey,
Prentice Hall.
Hawk, C., Jason, L. & Torres-Harding, S. (2007).
Reliability of a chronic fatigue syndrome
questionnaire, Journal of Chronic Fatigue
Syndrome, 13, 4, 41-66.
National Institute of Health (2005). National
Diabetes Statistics.
Hickie, I., Bennett, B., Lloyd, A., Heath, A. &
Martin, N. (1999). Complex genetic and
environmental relationships between
psychological distress, fatigue, and immune
functioning: A twin study. Psychological
Medicine, 29, 269-77.
Jason, L.A., Ropacki, M.T., Santoro, N.B.,
Richman, J.A., Heatherly, W., Taylor, R., Ferrari,
J.R., Haney-Davis, T.M., Rademaker, A.,
Dupuis, J.E., Golding, J., Plioplys, A.V. &
Plioplys, S. (1997). A screening instrument for
chronic fatigue syndrome: Reliability and
validity, Journal of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome,
3, 1, 39-59.
Jason, L.A., Taylor, R.R. & Kennedy, B.A. (2000).
Chronic fatigue syndrome, Fibromyalgia, and
Multiple Chemical Sensitivities in a
community-based sample of persons with
chronic fatigue syndrome-like symptoms.
Psychosomatic Medicine, 62, 655-663.
Invest in ME (Charity Nr. 1114035)
Jason, L.A., Taylor, R.R., Kennedy, C.L., Song,
S., Johnson, D. & Torres, S. (2001). Chronic
fatigue syndrome: comorbidity with
fibromyalgia and psychiatric illness. Medicine
& Psychiatry, 4, 29-34.
Jason, L.A., Torres-Harding, S., Friedberg, F.,
Corradi, K., Njoku, M.G., Donalek, J., Reynolds,
N., Brown, M., Weitner, B.B., Rademaker, A. &
Papernik, M. (2007). Non-pharmacologic
interventions for CFS: A randomized trial,
Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical
Settings, 14, 275-296.
Jason, L.A., Torres-Harding, S., Maher, K.,
Reynolds, N., Brown, M., Sorenson, M.,
Donalek, J., Corradi, K., Fletcher, M.A. & Lu, T.
(2007). Baseline cortisol levels predict
treatment outcomes in CFS nonpharmacologic
clinical trial. Journal of
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. 14, 39-59.
Pagani, M. & Lucini, D. (1999). Chronic fatigue
syndrome: A hypothesis focusing on the
autonomic nervous system. Clinical Science,
96, 1, 117-25.
Patarca-Montero, R., Mark, T., Fletcher, M.A. &
Klimas, N.G. (2000). Immunology of chronic
fatigue syndrome. Journal of Chronic Fatigue
Syndrome, 6, 3/4, 69-107.
Torres-Harding, S.R., Jason, L.A. & Turkoglu,
O.D. (2005). Family medical history of persons
with chronic fatigue syndrome, Journal of
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, 12, 25-35.
United States Census Bureau. (2000). Census
2000: Table DP-1, Profile of General
Demographic Characteristics. Retrieved June
26, 2008 from
www.census.gov/prod/cen2000/dp1/2kh00.p
df.
Walsh, C.M., Zainal, N.Z., Middleton, S.J. &
Paykel, E.S. (2001), A family history study of
chronic fatigue syndrome. Psychiatric
Genetics, 11, 123-8.
Page 11/74